Core V.2 LBS API
This document briefly goes through the Core V.2 LBS API. For more information about each API please read the corresponding header file.
The API
The LBS API consists of two parts, MapLibAPI and Nav2API. The MapLibAPI provides applications with rich map experiences including controls for seamless zooming and panning. It also gives third party developers the possibility to add their own content and controls on top of the map.
Nav2API is the back end for a full navigation application, including functionality for searching, routing, and storage of favourite locations.
The LBS API is developed according to the following design of interfaces and listeners.
Interfaces
An interface is a grouping of functionality such as searching. The operations on an interface are of two types, synchronous operations and asynchronous operations. Synchronous operations are the ones that can return immediately with the result of the operation. Asynchronous operations on the other hand will return the result in a call back at a later time.
Listeners
The purpose of a listener is to provide a way to get callbacks for the asynchronous operations defined in interfaces.
MapLibAPI
Start up
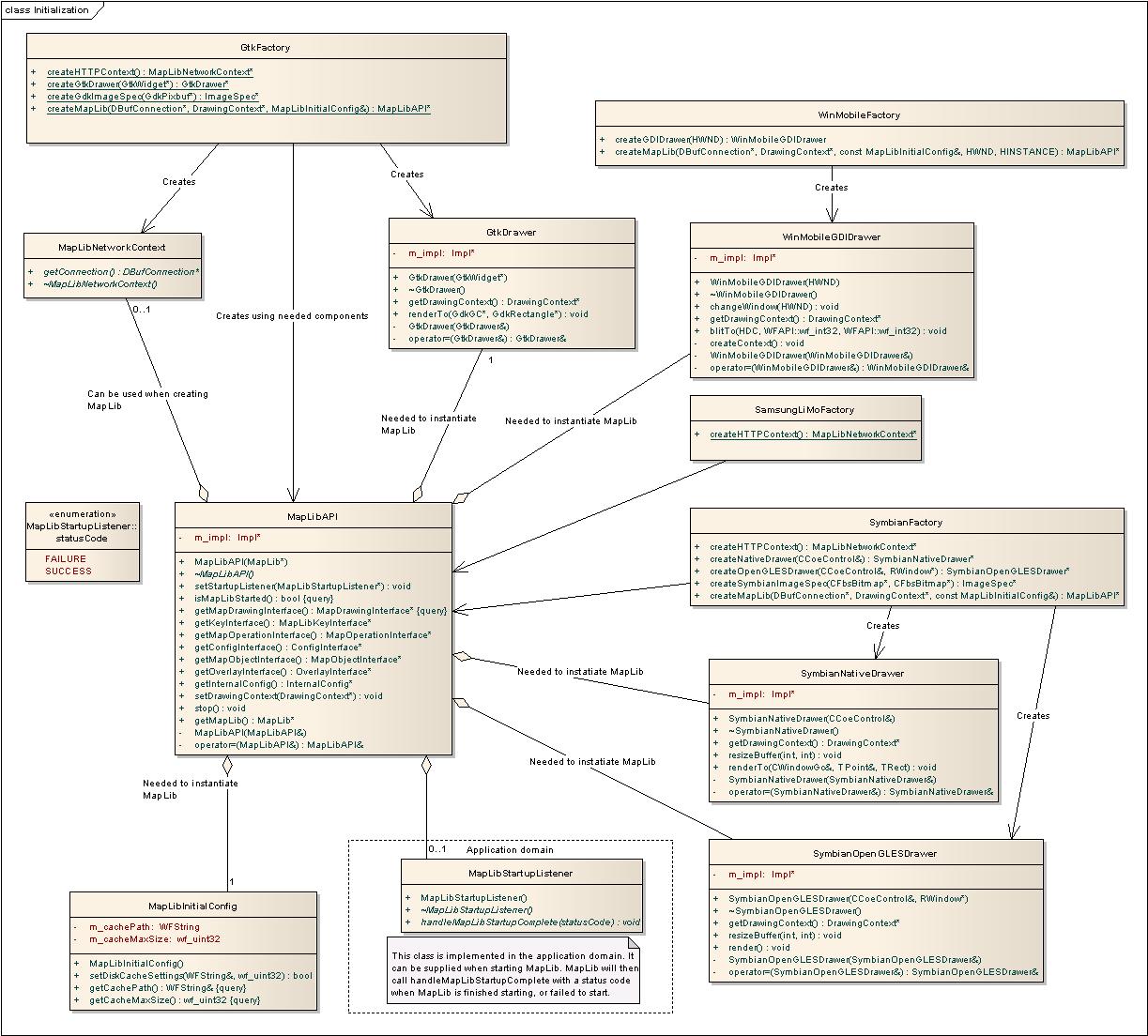
MapLibAPI requires three support classes in order to function. The first is a config class called MapLibInitialConfig, which describes MapLib-specific settings which can only be set at the point of instantiation, not at run-time.
The second one is a drawing context for MapLib. MapLib can use different map renderers for different platforms, and this class encapsulates this behavior. Since it is platform specific, it needs to be instantiated using a factory class which is implemented for the intended platform, for example GtkFactory for the Linux platform and WinMobileFactory for Windows Mobile.
The last class deals with the network connection necessary to download maps. This class is called DBufConnection. If MapLibAPI is intended to be used as a standalone, i.e. without a connection to Nav2API, an instance of such a class can be instantiated using factory methods. The DBufConnection is then obtained in two steps:
- Create a
MapLibNetworkContext, for instance by callingcreateHTTPContext()inSamsungLiMoFactoryfor SamsungLiMo specific network support or inSymbianFactoryfor Symbian specific network support. - Get a
DBufConnectionby callinggetConnection()on the network context. Be sure to only release theMapLibNetworkContextonce MapLib is properly shutdown.
MapLibAPI itself can then be created using createMapLib() in the factory class, supplying the resulting DbufConnection().
If you intend to use MapLibAPI together with Nav2API instead (which is recommended if Nav2API is used), you can get the network connection from Nav2API using the getDBufConnection() function, once Nav2LibAPI is properly started. Then supply the DBufConnection from Nav2LibAPI into the createMapLib() factory function. Once this is done, MapLibAPI must be connected to Nav2LibAPI by calling Nav2LibAPI::connectMapLib().
Once instantiated, MapLib will need to initialize itself by downloading various information from the server. This process is automatically started after the factory function createMapLib() is called. It is possible to register a listener to get notified once MapLib is properly started by calling MapLibAPI::setStartupListener(MapLibStartupListener* startupListener).
MapLib Core
The core of MapLibAPI consists of various interfaces that are used to interact with a customizable map view.
These are all accessed from the MapLibAPI class, and they all require that MapLibAPI is properly initialized. Notification of this state can be registering a class derived from MapLibStartupListener in MapLibAPI::setStartupListener().
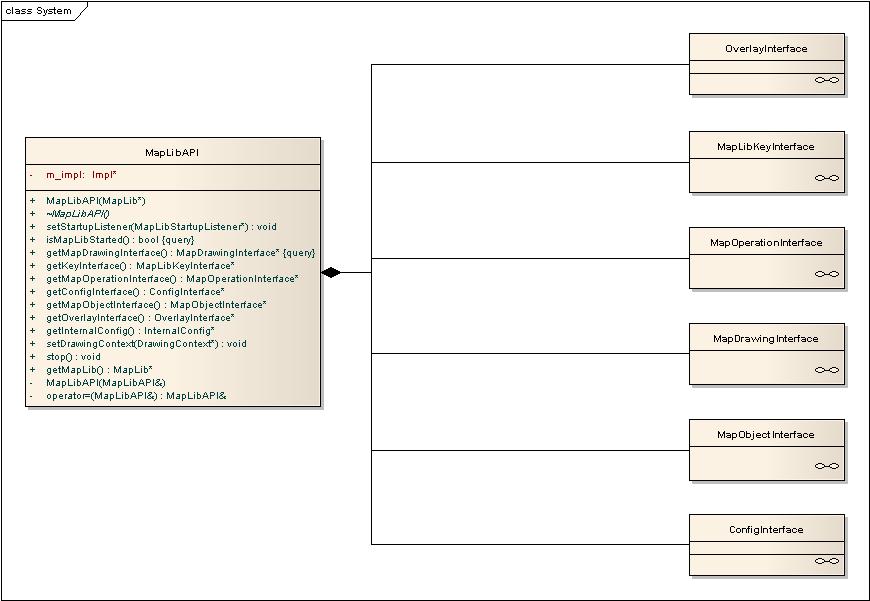
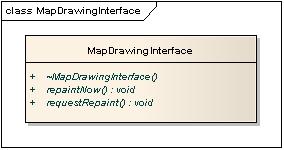
Drawing Interface
The drawing interface is a very simple interface that exposes drawing related operations. It has support for triggering either immediate or delayed redraws of the map.
See MapDrawingInterface.h for more information about this API.
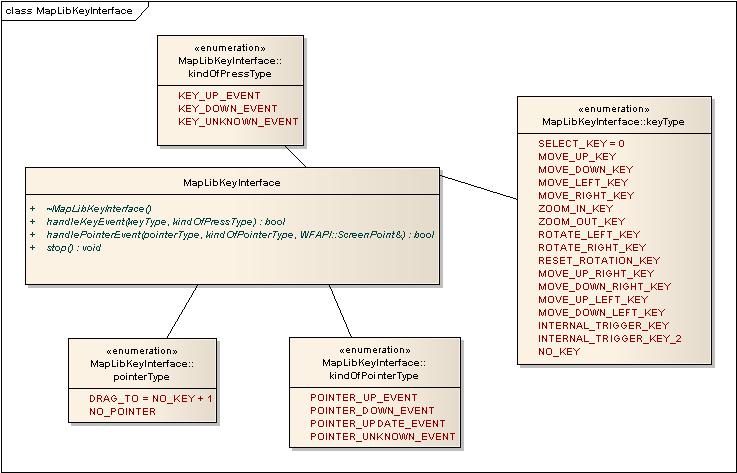
Key Interface
The key interface is used to forward key input and pointer events to MapLib, so that it can respond to user input.
See MapLibKeyInterface.h for more information about this API.
Map Operation Interface
This class supports various operations on a map, such as zooming, rotating and moving it.
See MapOperationInterface.h for more information about this API.

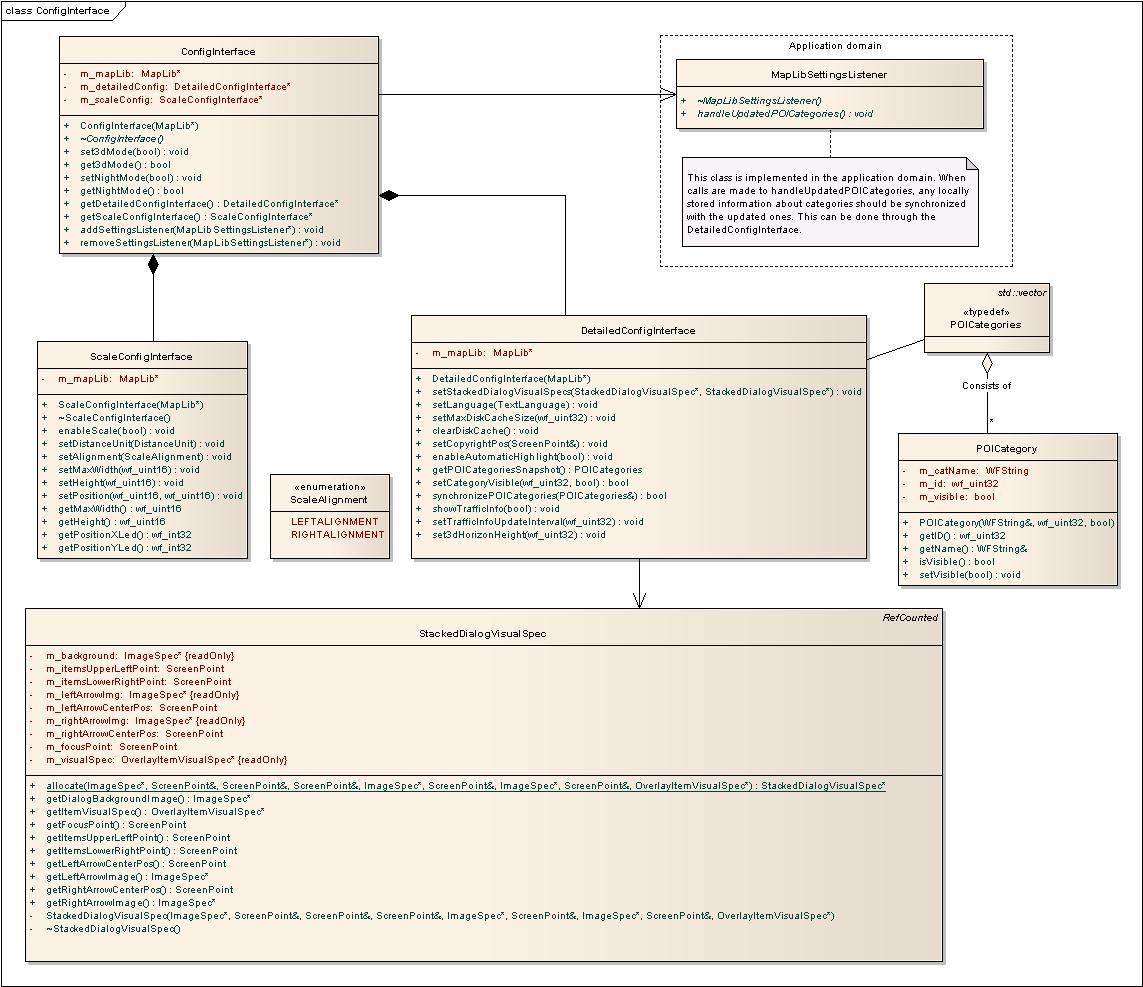
Configuration interface
Use this class to configure MapLib to your liking. Here you can enable 3d mode, night mode and other features.
See ConfigInterface.h for more information about this API.
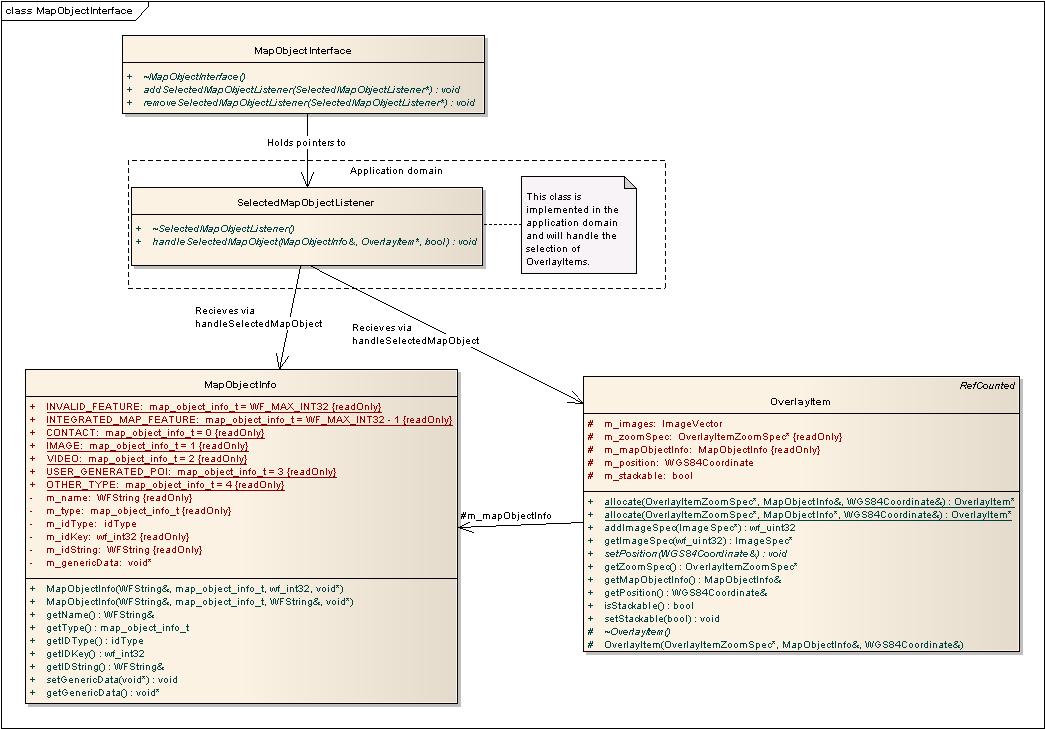
Map Object interface
This interface can be used to add callbacks that are notified whenever objects are selected on the map.
See MapObjectInterface.h for more information about this API.
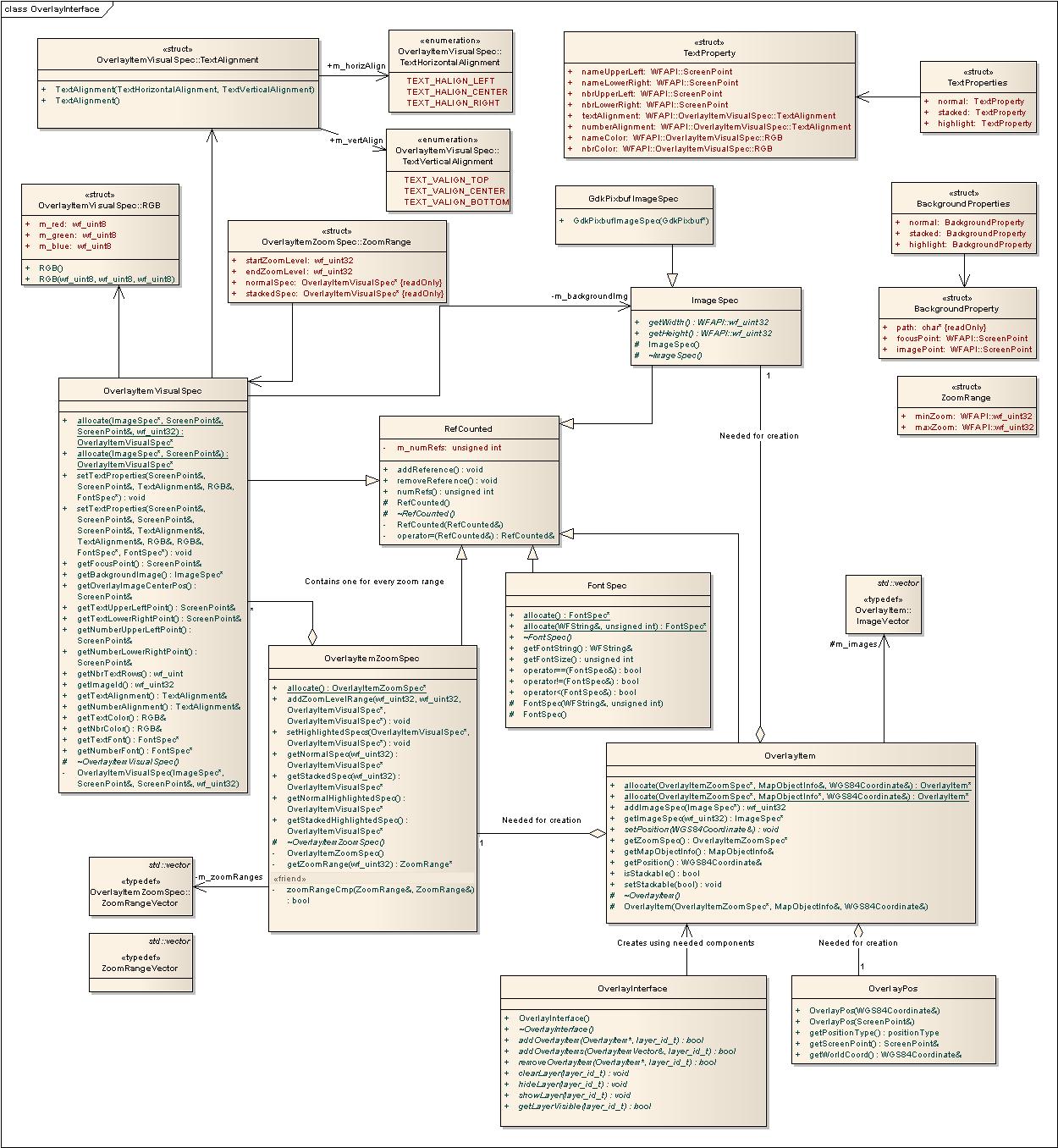
Overlay interface
With this interface you can add custom objects to the map view. Multiple layers are supported.
See OverlayInterface.h for more information about this information.
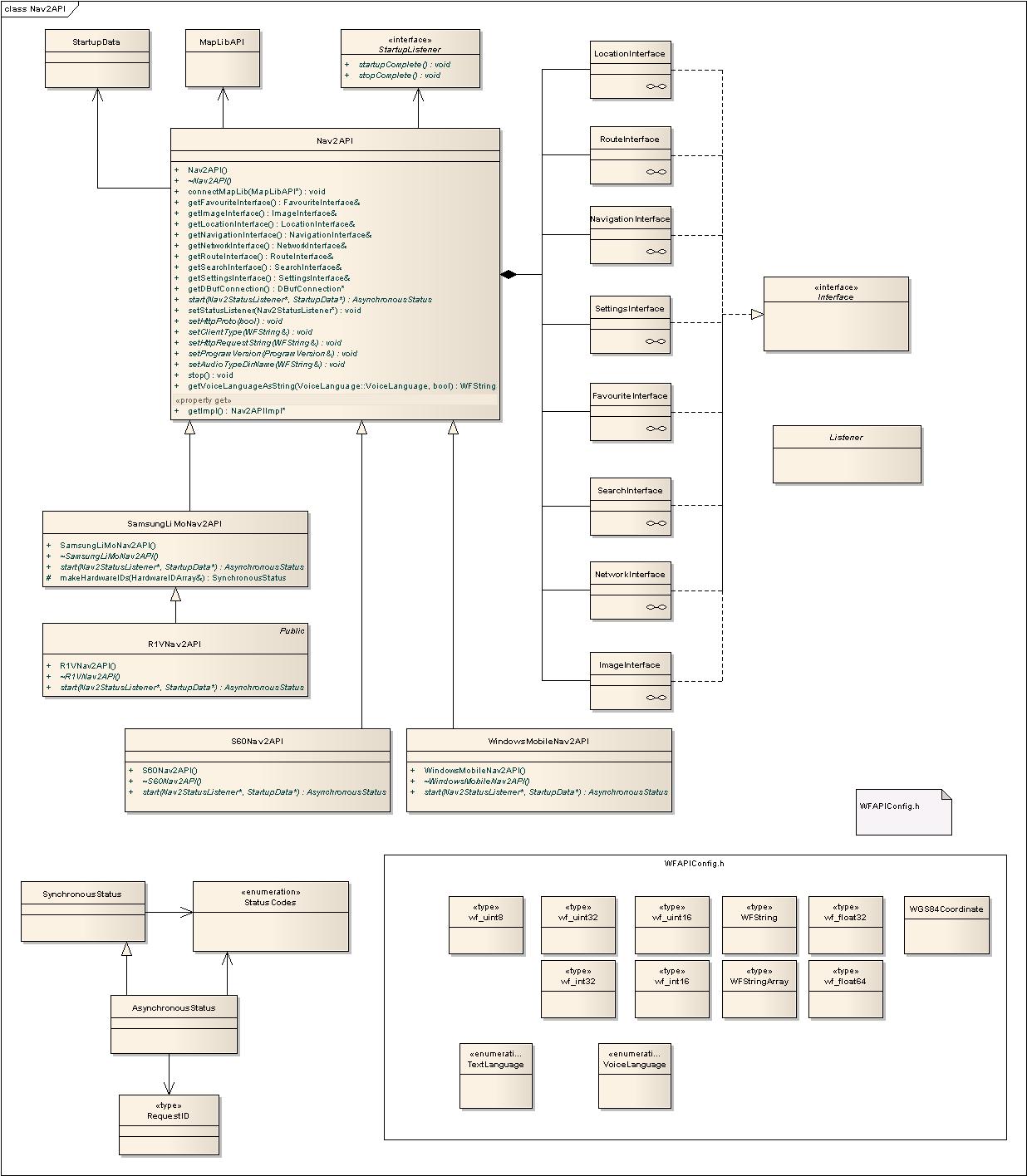
Nav2API
The Nav2API has a main class called Nav2API that holds all the parts of the API. These parts are described in the sections below. A MapLibAPI object can be connected to a Nav2API object using the connectMapLib function in Nav2API, a connected MapLib uses Nav2API for server communication and for storage of settings.
Startup
The construction of Nav2API is two phased. First the Nav2API object is made then the asynchronous start function is called with the initialization data and a Nav2StatusListener object. After the Nav2API has started up, the Nav2StatusListener is called.
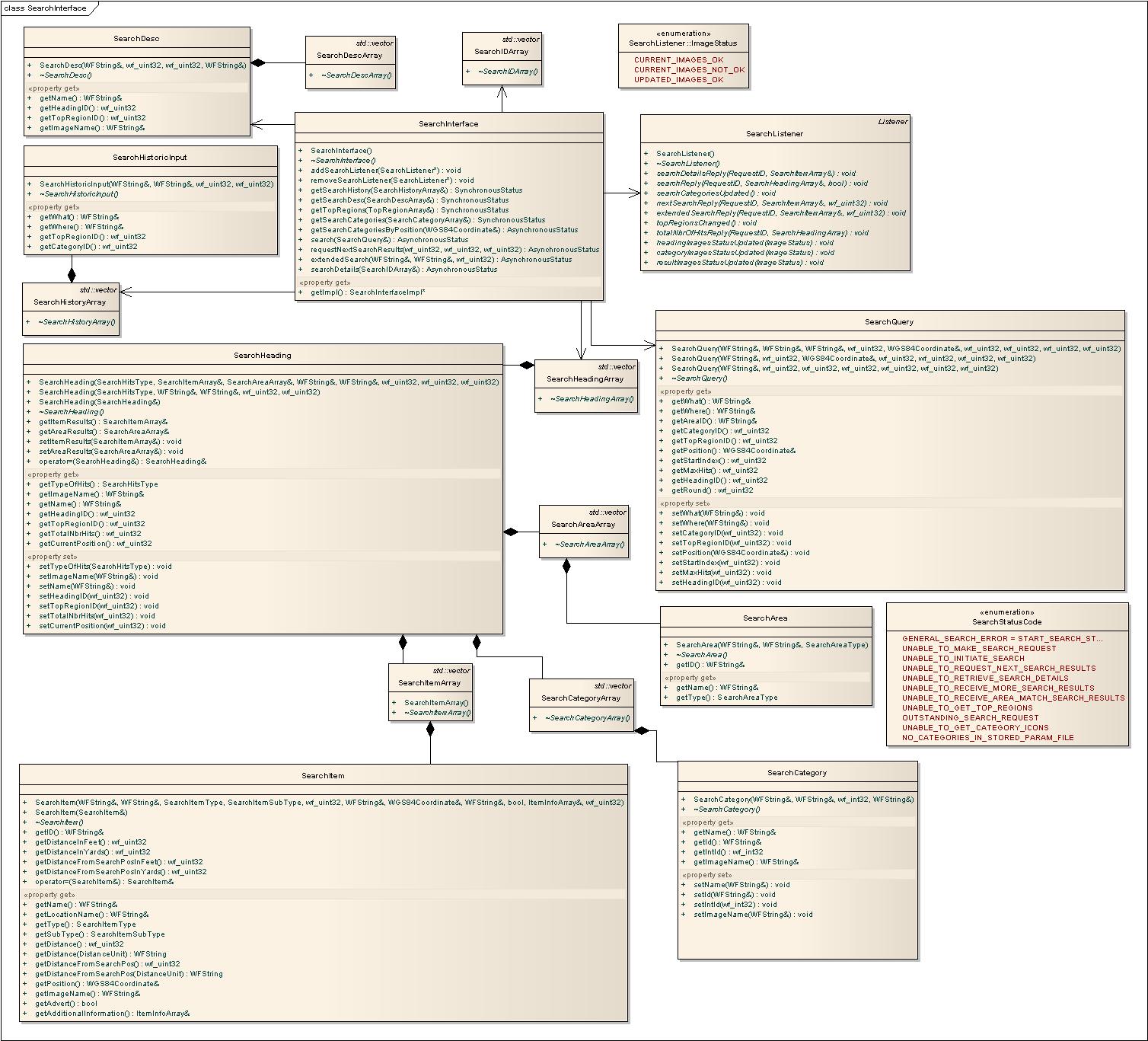
Search Interface
The search is based on two text input fields, what and where, and a selectable region as user input. The selectable regions can be retrieved using the getTopRegions() function. When the user has made the input it is put into a SearchQuery object and sent as an asynchronous request using the search function. The result is then received in the SearchListener::searchReply() function.
The search result is divided into several SearchHeadings which in turn contains a list of SearchItems or SearchAreas. The SearchItems describes a point hit and SearchAreas describes a selection of areas to be selected and searched again to get SearchItems.
Previous search inputs are stored in Nav2API and are available through the getSearchHistory() function. The available SearchHeadings can be retrieved using the getSearchDesc() function.
See SearchInterface.h for more information about the Search API.
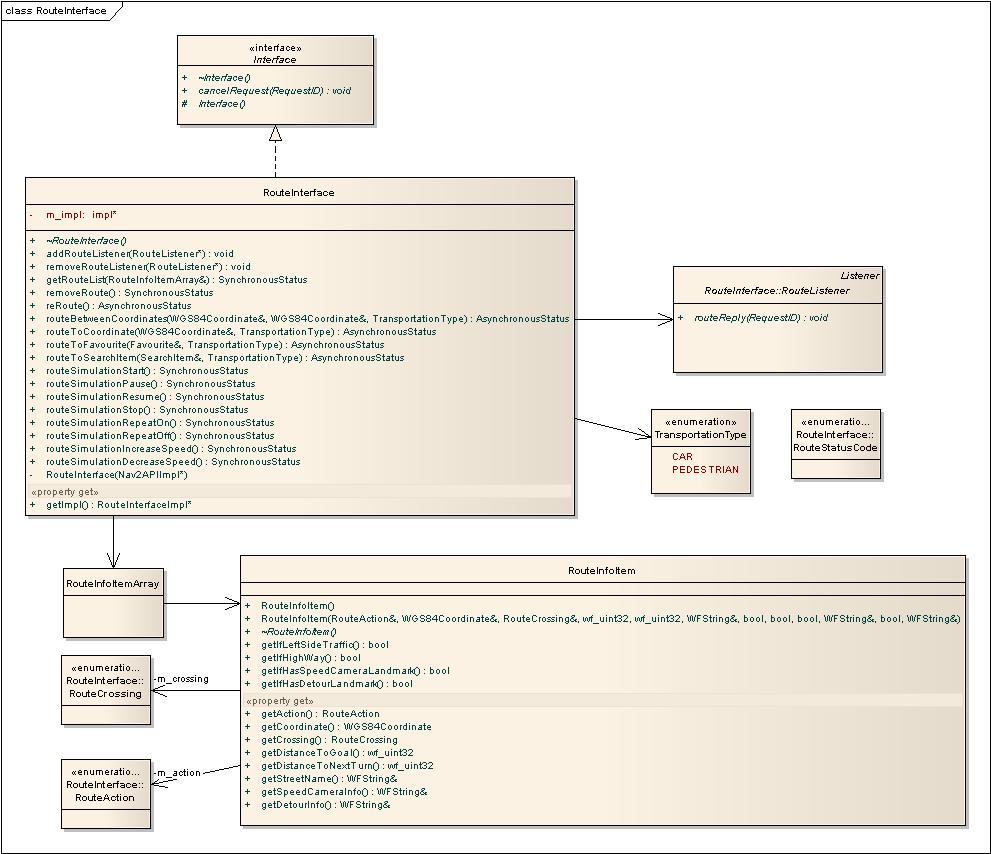
Route Interface
In the RouteInterface routes are made from point A to point B. A route can be made using the asynchronous routeBetweenCoordinates() and routeToCoordinate() functions. When the RouteListener::routeReply() function has been called the route itinerary is available via the getRouteList() function. The current route in RouteInterface is used by the NavigationInterface` for turn by turn navigation.
See RouteInterface.h for more information about the route API.
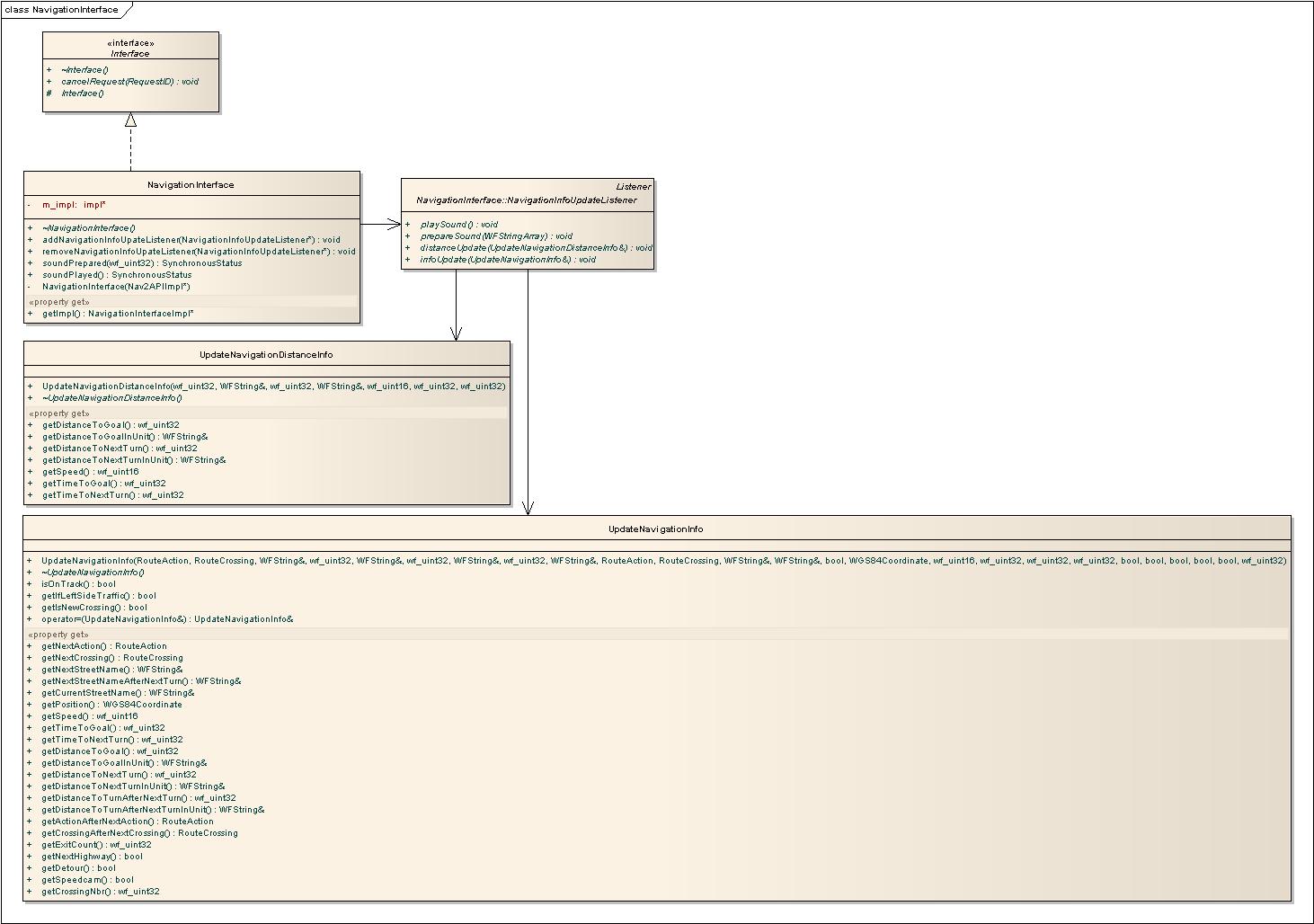
Navigation Interface
The NavigationInterface uses the current route in the RouteInterface to give turn by turn instructions with continuous updates to the NavigationInfoUpdateListener. See NavigationInterface.h for more information about the Navigation API.
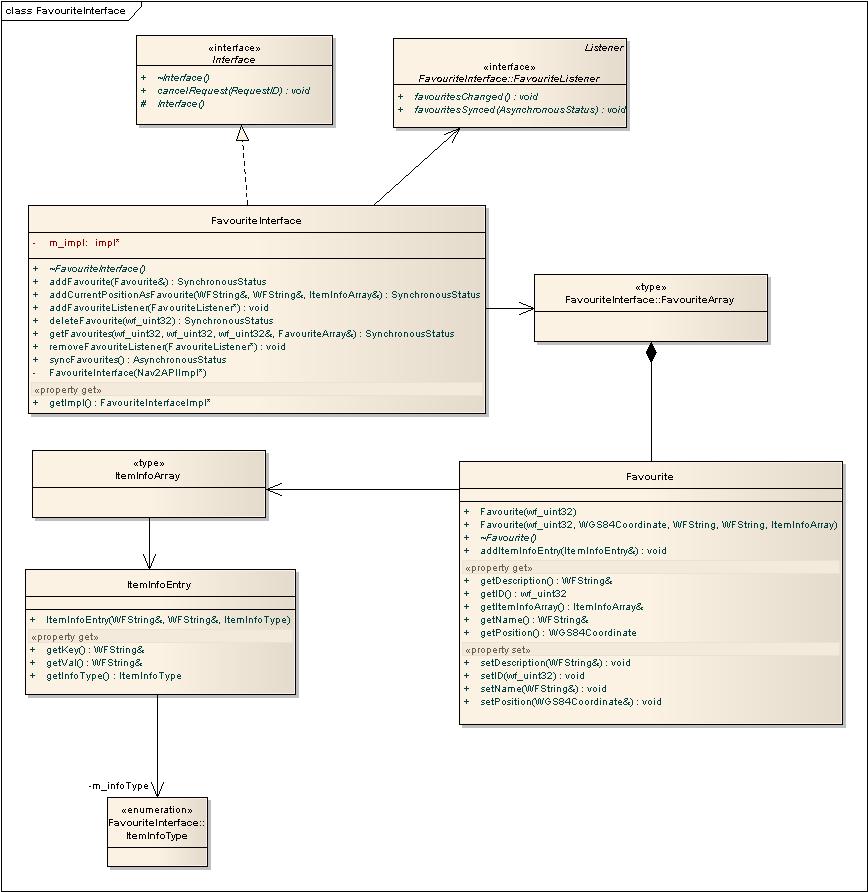
Favourite Interface
Nav2API provides functionality for favourite management and storage of favourite locations. Each favourite contains information in the form of a name, description, position and some optional additional information.
See FavouriteInterface.h for more information about this API.
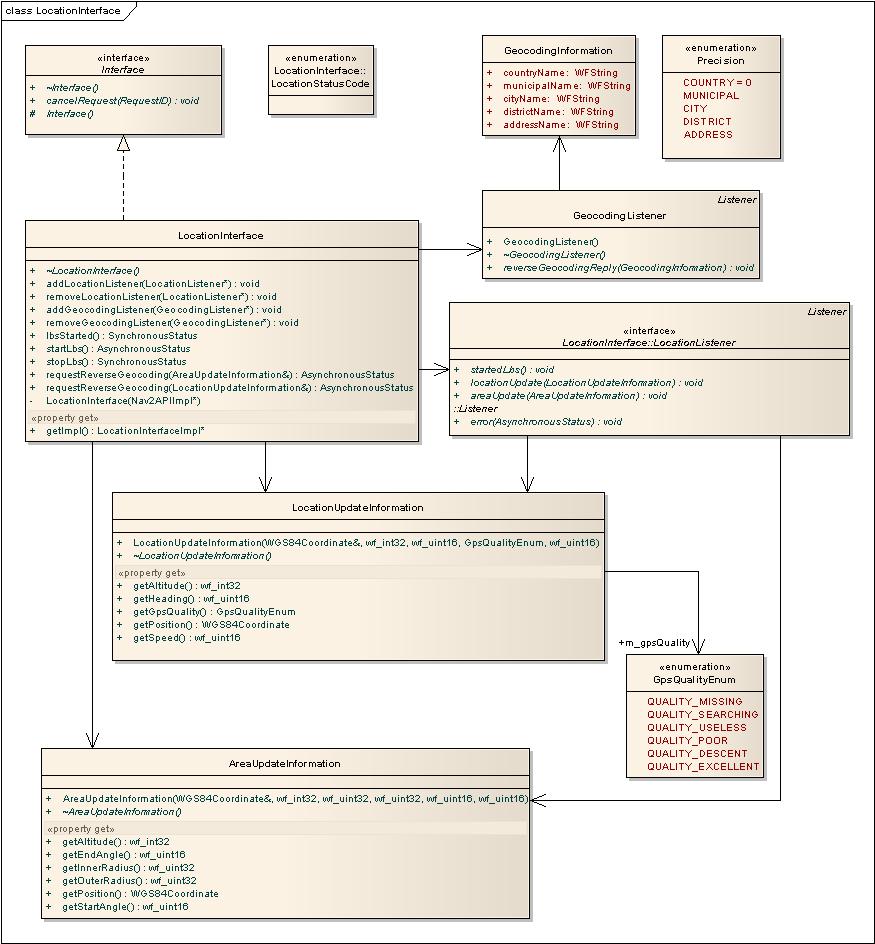
Location Interface
LocationInterface is the source for position updates from either GPS or Cell ID depending on what service is available.Through this interface it is also possible to do reverse geocoding.
See LocationInterface.h for more information about this API.
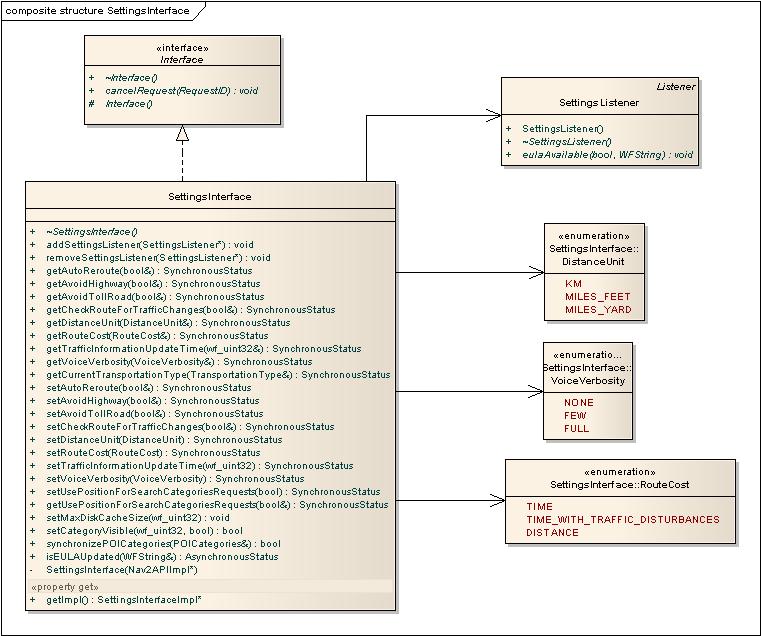
Settings Interface
In SettingInterface the Nav2API can be configured while the application is running. There is a group of settings that is for the connected MapLibAPI and the settings are set in the connected MapLibAPI object if one is set. Setting are stored in Nav2API between application restarts.
The following settings are set in the connected MapLibAPI:
setMaxDiskCacheSizesetCategoryVisiblesynchronizePOICategories
See SettingsInterface.h for more information about this API.
Network Interface
Here the preferred network link can be set and tested. Depending on the platform the NetworkID can be different identifications like PDP id and API id.
See NetworkInterface.h for more information about this API.
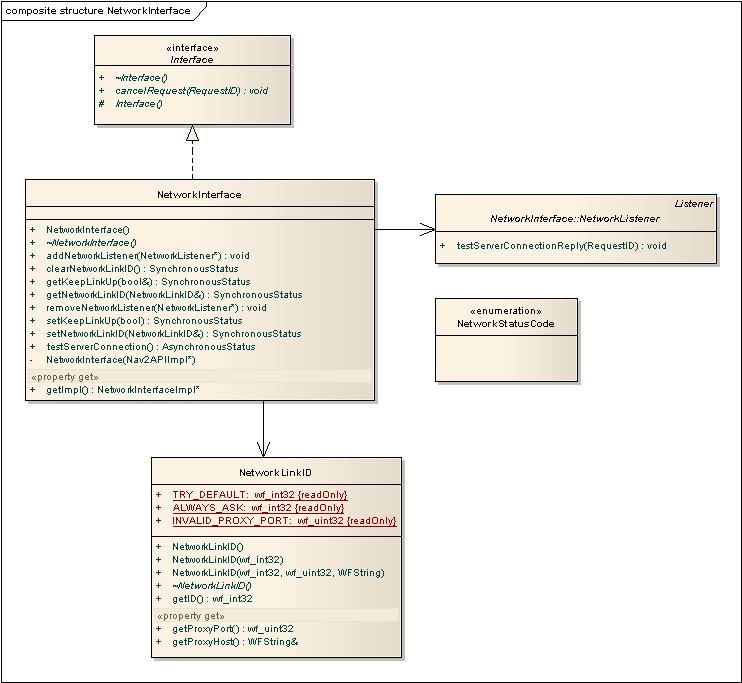
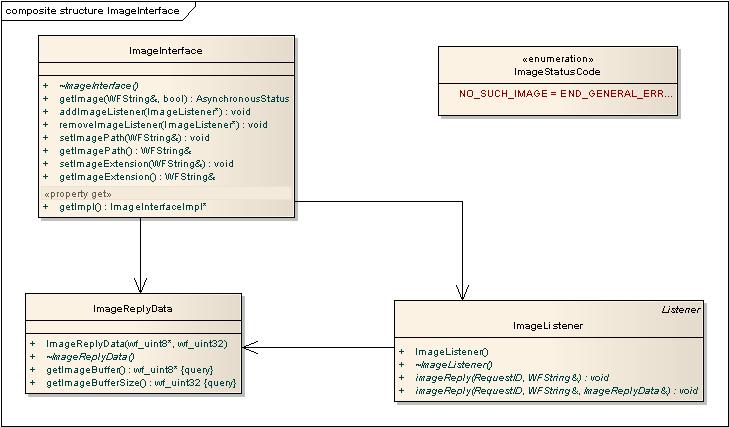
Image Interface
Image names from SearchItems or SearchDescs can be retrieved in this interface. The image name is sent in to the getImage function and received in the ImageListener when the image is downloaded. Images can be retrieved in a buffer or as a downloaded file.
See ImageInterface.h for more information about this API.
Tunnel Interface
The tunnel interface can be used to tunnel data from the server and it can be any kind of data.
See TunnelInterface.h for more information about this API.
Billing Interface
An interface to control billing transaction and verify a transaction has succeeded completely.
See BillingInterface.h for more information about this API.